Tanzania is one of the top travel destinations for African safaris, and many people are curious to learn where it is. The country is renowned for its wildlife, beaches, and iconic sights, and understanding its location helps explain why it became prominent in Africa for tourism, culture, and geography.
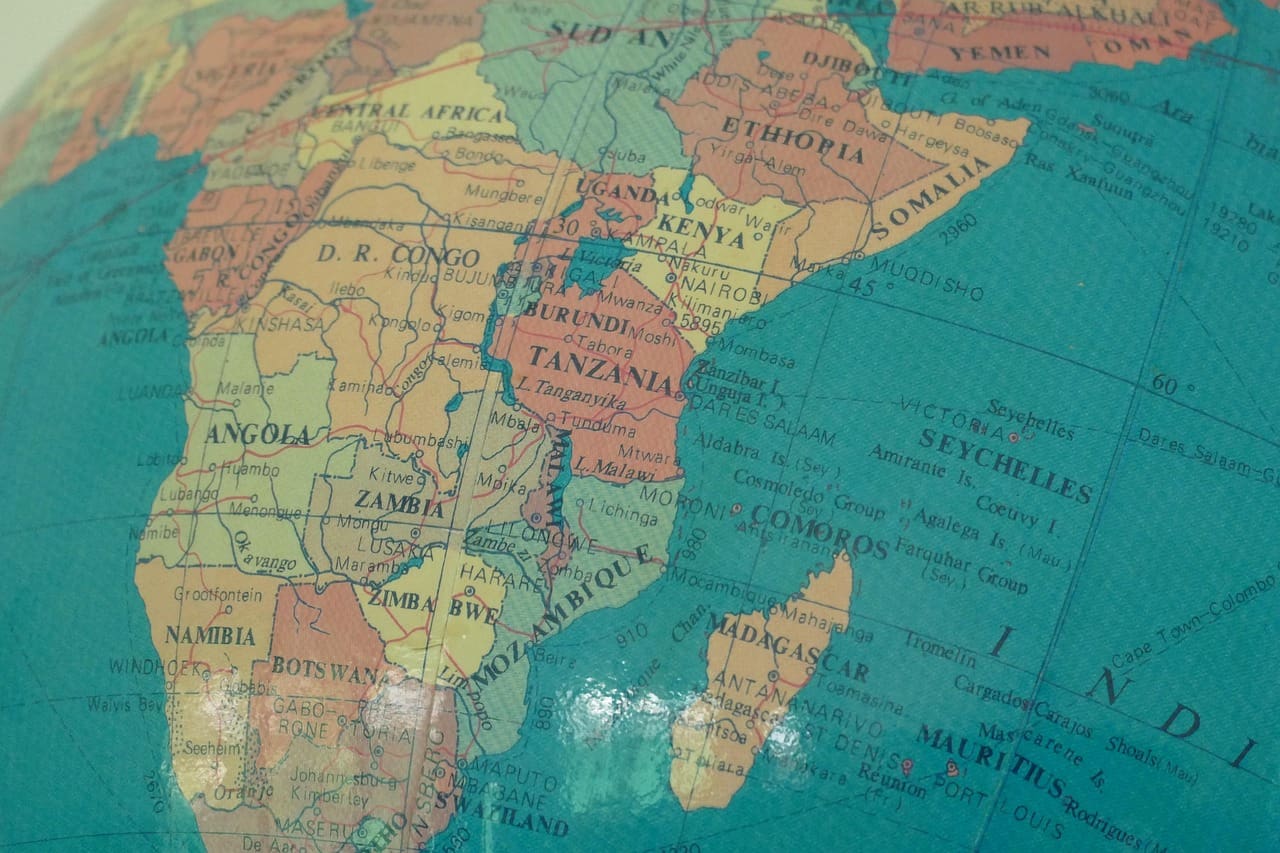
Tanzania is an East African nation which is located on the eastern coast of Africa. It is near the equator and experiences warm temperatures year-round. Tanzania is situated between 1° and 12° south of the equator and between 29° and 41° east of the equator, placing it within the equatorial belt. The country’s average elevation is approximately 200 metres (650 feet). This position has endowed Tanzania with diverse ecosystems, including tropical beaches and high-altitude areas, making it a must-visit on any travel itinerary.
Where Is Tanzania In Africa?

A helpful way to explain Tanzania’s location is to situate it within its African context. To answer the question of where Tanzania is in Africa, the country is located on the eastern side of the African continent, along the Indian Ocean coast. Tanzania is part of the East African region, which comprises countries that share a common geography, culture, and trade connections.
Tanzania’s immediate neighbours are Kenya and Uganda to the north, Rwanda and Burundi to the northwest, the Democratic Republic of the Congo on the western side of Lake Tanganyika, and Zambia, Malawi, and Mozambique to the south. On the eastern side, Tanzania borders the Indian Ocean, resulting in a long coastline and access to major maritime routes.
What Are Some Key Facts About Tanzania?
Tanzania’s position in Africa is particularly notable, as it serves as a natural bridge between East, Central, and Southern Africa, linking trade routes, cultures, and ecosystems across the region.
Some essential facts concerning Tanzania are:
- Region: East Africa
- Official name: United Republic of Tanzania
- Population: Over 60 million people
- Geographic position: It is located on the eastern coast of Africa, with the Indian Ocean as its neighbour.
- Standard greeting: “Jambo” or “Habari”
- Neighbouring countries: Neighbouring states: Kenya and Uganda to the north; Rwanda and Burundi to the northwest; the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west, and Zambia, Malawi, and Mozambique to the south
- Capital city: Dodoma
- Largest city: Dar es Salaam
- Major city centres: Dar es Salaam, Arusha, Mwanza, and Dodoma
- Political history: The country was formed in the year 1964, and it merged mainland Tanganyika and Zanzibar under the leadership of Julius Nyerere
- Currency: Tanzania Shilling (TZS)
- Climate: Tropical, with regional variations
- Time zone: East Africa Time (UTC+3)
- Main industries: Agriculture, tourism, mining, and services
- Driving side: Left
- Electrical plug type: Type D (220v – 240v) and G (230V)
- Visa policy: Most visitors require a visa on arrival or an e-visa
- Religion: Majorly Christianity and Islam
Given its central location, Tanzania serves as a gateway to various African regions, facilitating trade, tourism, and cultural exchange. It also borders other major African landmarks, such as Lake Victoria, the Serengeti Plain, and Mount Kilimanjaro, additionally increasing its geographic significance.
What Are The Geographical Features That Define Tanzania
Tanzania’s geographic location supports some of Africa’s most renowned natural landmarks. Vast plains, highlands, lakes, and coastal regions characterise the country. This difference in land, which was caused by the country’s position in the East African Rift System, has produced some of the differentiating areas, such as:
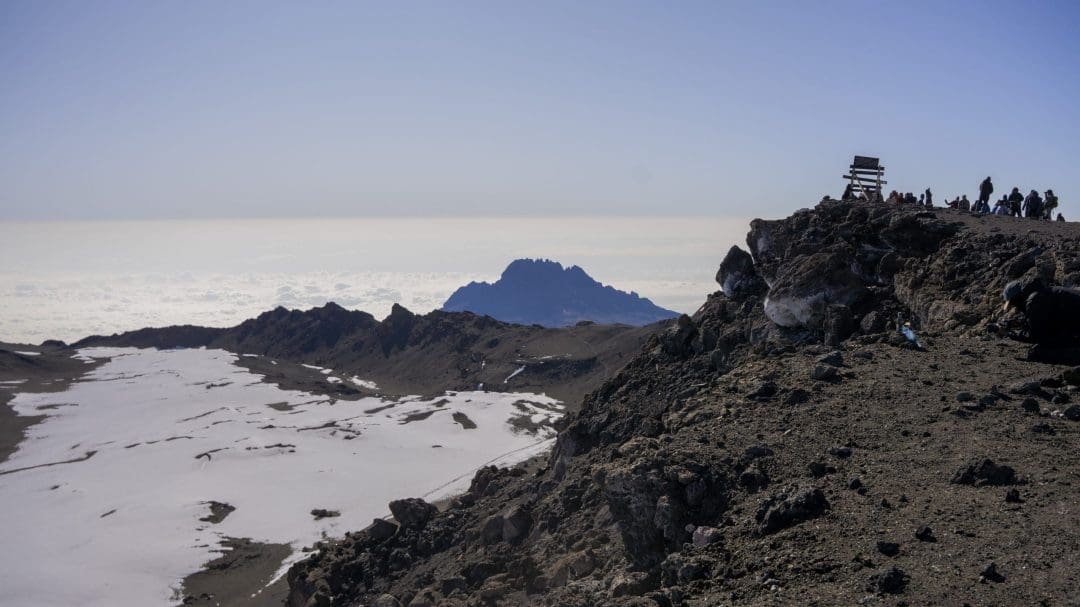
- Mount Kilimanjaro (5,895 metres / 19,341 feet), Africa’s highest peak
- The Serengeti Plain, famous for wildlife migration
- Lake Victoria, Africa’s largest lake
- Lake Tanganyika, one of the world’s deepest lakes
- Tropical islands like Zanzibar
Due to this diversity, Tanzania supports both safari tourism and adventure travel. Many visitors choose to explore national parks or climb Mount Kilimanjaro as part of their holiday activities.

What Is The Capital City Of Tanzania?
Dodoma is the capital of Tanzania and is situated in the centre of the country. It became the official capital only in 1974, and the aim was to establish a more central administrative centre.
However, the largest city and the significant economic centre is Dar es Salaam, which is situated on the coast of the Indian Ocean. Dar es Salaam is also Tanzania’s principal port and a frequent point of entry for international travellers.
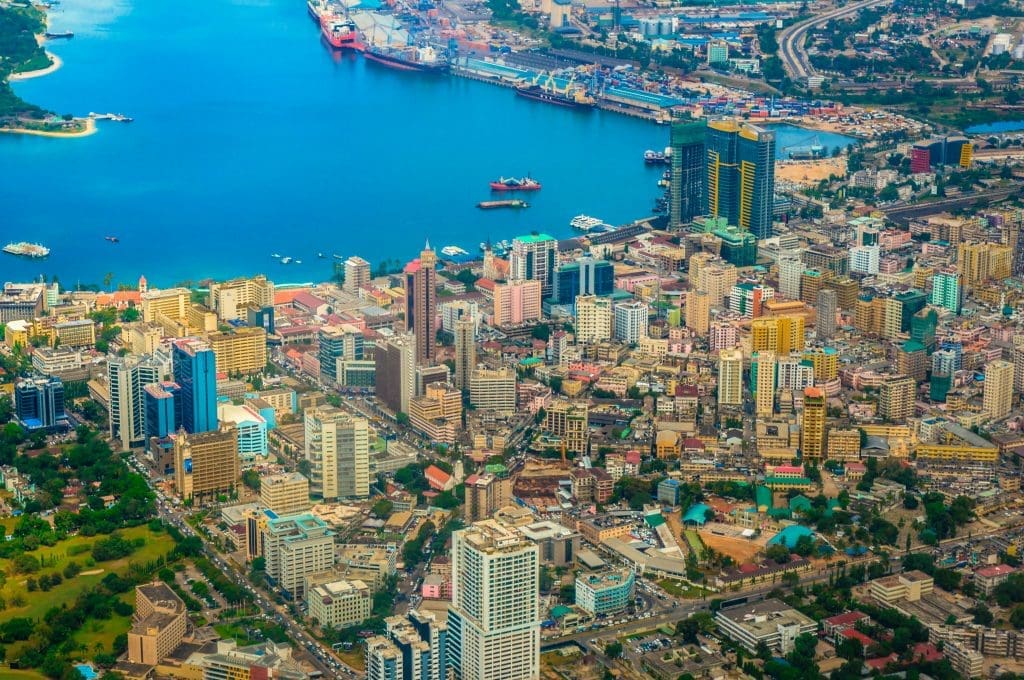

Other major cities to be mentioned are:
- Arusha – the gateway to northern Tanzania safaris
- Mwanza – on the shores of Lake Victoria
- Mbeya – in the southern highlands
What Language Is Spoken In Tanzania?
Knowledge of the language spoken in Tanzania helps travellers relate better to locals. There are two official languages in Tanzania, which are:
- Swahili (Kiswahili) – the national language
- English – widely used in business, tourism, and education
Swahili is a language spoken in East Africa and is Tanzania’s national language, uniting various ethnic communities. English is also widely spoken in tourist areas, but it is always advisable to learn some Swahili phrases.
What Are The Climate Zones Of Tanzania?
Tanzania has many different climate zones. The country lies on or near the equator and spans a wide range of elevations. The coastal areas are often hot and humid, while higher elevations are typically cooler.
The central zones are:
Coastal Areas
Its coastline, which includes Dar es Salaam and Zanzibar, experiences a hot, humid tropical climate.
- Average temperatures are 26°C–32°C (79°F–90°F)
- The humidity is high all year round
- It experiences heavy rainfall during the long rains (March–May)
This is a great destination for a beach holiday, with sandy beaches and excellent facilities.
Highlands
The northern and southern highlands in Tanzania have a cool, temperate climate.
- Average temperatures are 15–25°C (59–77°F)
- Lowers temperatures due to altitude.
- Highly fertile soils for agriculture.
These are trekking places and agricultural communities.
Central Plateau
A semi-arid climate with low, erratic rainfall is experienced on the central plateau, including Dodoma and many other central areas.
- The days are usually hot with cool nights
- Dry lands with low and unpredictable rainfall
- Temperatures can reach between 20°C and 30°C
- Livestock grazing and drought-resistant crops
Great Lakes Regions
The regions around Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika and Lake Nyasa have a hot and humid tropical climate.
- Higher precipitation compared to inland areas
- Hot all year round
- Fosters lush vegetation and fisher communities
This climate is crucial for agriculture and freshwater ecosystems.
Mountain Regions
Mountainous areas, including Kilimanjaro, Meru, the Eastern Arc Mountains, and others, are characterised by alpine and montane climates.
- Temperature decreases with height above sea level
- Mount Kilimanjaro has freezing weather at the summit
- Different layers of vegetation between the rain forest and the alpine desert.
- Attractions for climbers, hikers and nature enthusiasts.
Savannah Zones
A tropical savannah climate, such as that of the Serengeti Plain and the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, characterises vast areas of Tanzania.
- Clear wet and dry seasons
- The ideal conditions for the migration of wild animals
- Temperatures range between 20–30°C (68–86°F)
Tanzania’s variety makes it a year-round destination, depending on your interests.
Why Is Tanzania So Famous?
Tanzania is known for its natural wonders and wildlife activities. Some of the best-known attractions are:
- Serengeti National Park, which is famous for the Great Wildebeest Migration
- Ngorongoro Crater, a UNESCO World Heritage Site
- Mount Kilimanjaro, the world’s tallest free-standing mountain
- Pristine beaches in Zanzibar
The various attractions have helped make Tanzania one of the most visited African countries for safari trips and adventure tours. Many travellers book various Tanzania safari tours to experience wildlife in its natural environment.
Where Is Serengeti National Park In Tanzania?

The Serengeti National Park is situated in northern Tanzania, near the border with Kenya. It is a part of a larger ecosystem that extends to the Maasai Mara in Kenya.
This region is known for:
- Open grasslands
- Large predator populations
- Annual wildebeest migration
The Serengeti National Park is readily accessible from Arusha, a central safari hub.
What Is The Best Time to Visit Tanzania?
Knowing the perfect time to visit Tanzania will enhance your experience, whether you’re on safari, mountain climbing, or taking a beach holiday in Zanzibar.
Dry Seasons (June-October and January-February)
Popular months for travel are during the dry seasons:
June to October:
The Serengeti National Park and the Ngorongoro Crater are ideal for wildlife viewing, as the skies are clear and the temperatures are low.
January to February:
The weather is often dry and mild during the day. The landscape is extremely green due to recent rainfall, making it a great time for a birdwatching and strolling safari.
In the dry months, the roads and trails are easier to drive on, and outdoor activities such as balloon safaris, guided hikes, and beach vacations continue uninterrupted.
Wet Seasons (March to May & November to December)
Tanzania has two rainy periods:
March to May (Long Rains)
There are heavy rainfalls, particularly in March and April. Safari tracks and hiking trails may become clogged with mud or be closed. But the scenery becomes so lush and wonderful.
November to December (Short Rains)
Although the season has increased rainfall, it is not as disruptive as the long rains and may still be an excellent opportunity to travel with fewer crowds and at a lower cost.
Special Considerations
Climbing Mount Kilimanjaro
If your trip includes hiking to Uhuru Peak, January-March and June-October are the most favourable times to visit, as it is unlikely to be raining and the weather is generally clearer.
Zanzibar Beach Escapes
The weather lull between June and October, or between December and February, provides warm, sunny days that are excellent for beach activities, snorkelling, and island visits.
How To Get To Tanzania

Most international travellers enter Tanzania by air, with several well-connected entry points serving different parts of the country.
The major international gateways are the Julius Nyerere International Airport (DAR) in Dar es Salaam and the Kilimanjaro International Airport (JRO) near Arusha, the gateway of choice for visitors planning safaris in northern Tanzania or climbing Mount Kilimanjaro.
The Abeid Amani Karume International Airport (ZNZ) in Zanzibar also offers international flights to select destinations, allowing visitors to travel directly to the coast or islands.
The neighbouring countries can be used to travel to Tanzania by overland via various routes. These are the paths frequented by local tourists and backpackers.
Regular ferry transport has been established between Dar es Salaam and Zanzibar, making sea travel popular and a scenic option for visitors booking mainland and beach holiday trips.
Why Visit Tanzania in Africa?
Tanzania offers a rare blend of wildlife, landscapes, culture, and adventure. From safaris to mountain treks and coastal relaxation, the country suits many travel styles.
It is one of the most ideal destinations in East Africa due to its location, security, and tourism infrastructure.
Is Tanzania a Good Country for First-Time Visitors to Africa?
Tanzania is often recommended to first-time visitors to Africa because its tourism infrastructure is well-developed, political conditions are stable, and activities range from safaris, cultural tours, mountain trekking, and beach holidays.
Where Is Zanzibar Located in Tanzania?
Zanzibar is an island archipelago located off the eastern coast of Tanzania in the Indian Ocean. It is located in the United Republic of Tanzania and can be easily reached by short flights or by ferry from Dar es Salaam.